나만 알고싶은 Vagrant 사용법
Vagrant 사용법
퍼블릭 클라우드를 이해하기 위해 지난 시간 대표적인 Amazone AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google GCP 3가지 퍼블릭 클라우드의 특징을 확인했다. 이번 챕터에서는 Vagrant를 통해서 자신의 PC에서 가상화 시스템을 운영하면서 IaC (Infrastructure as Code)에 대한 간단한 콘셉트를 이해하도록 한다.
IaC (Infrastructure as Code)

인프라스트럭처 시스템은 서버, 네트워크, 보안, 스토리지 등 다양한 서비스를 안정적으로 운영하기 위해 발전했으며, 이를 관리하기 위한 복잡도 역시 증가하였다. 하나의 애플리케이션을 구성하고 이를 배포하기에 수 많은 시스템 간의 연계 및 구성이 필요하고 빠르게 변화하는 IT 산업에서 민첩성이 중요하게 대두되었다. 하지만 상대적으로 개발에 비해 인프라는 한번 구성된 이상 시스템 변경이 어렵고 느리기 때문에 프로덕션 환경에서의 기존 인프라 환경의 유지는 효율성과 속도에 영향을 끼친다.
IaC는 이를 개선하기 위해서 수정적인 관리 시스템을 탈피하고 스크립트, 코드, 자동화 툴을 사용하여 전체 인프라스트럭처 시스템을 말한다. 코드를 통해 인프라시스템을 운영하기 때문에 반복적인 작업에 있어서 자동화가 가능하고 인적 실수를 줄일 수 있다. 특히나 퍼블릭 클라우드가 대중화되면서 서버라는 자원을 누구나 쉽게 접근할 수 있고, 친숙한 코드 형태로 작성하기 때문에 인프라에 대한 자세한 내용을 신경 쓰지 않고 빠르게 애플리케이션을 개발하고 배포할 수 있다.
나만의 클라우드 Vagrant
Vagrant의 사전적인 의미는 “부랑자”/“정처없는 사람”을 뜻한다. 가상 환경을 효과적으로 만들고 테스트하는 유연한 환경에서 지어진 이름이라고 명명되었다고 생각할 수 있다. Vagrant가 지원하는 가상화 기술은 다음과 같다.
- VirtualBox
- VMware
- KVM
- Linux Container (LXC)
- Docker
Vagrant를 통해 코드를 작성해두면, 가상화 환경을 만들고 실행하는데 있어서 빠르게 진행할 수 있다는 장점을 가지고 있다.

Vagrant는 2010년 3월에 “Mitchell Hashimoto”가 시작한 오픈소스 프로젝트이며, 2012년 11월 HashiCorp 설립하여 다양한 오픈소스 기술을 개발 및 운영하고 있다.
Vagrant 설치하기
기본적으로 Vagrant을 사용하기 위해서는 VirtualBox가 같이 설치되어 있어야 한다. MacOS에서는 다음과 같이 설치한다.
$ brew install --cask virtualbox virtualbox-extension-pack vagrant$ vagrant -v
Vagrant 2.2.14Vagrant 기본 명령어
Vagrant를 사용하기 위해서 반드시 알아야 하는 기본 명령어들이 있다. 다음을 기억하고 넘어가도록 한다.
- vagrant init
- 베이그런트를 프로비저닝 하기 위한 Vagrantfile을 생성한다.
- vagrant up
- 작성된 Vagrantfile을 바탕으로 프로비저닝을 진행한다.
- vagrant halt
- 베이그런트에서 관리하는 가상 머신을 종료한다.
- vagrant destroy
- 베이그런트에서 관리하는 가상 머신을 삭제한다.
- vagrant ssh
- 베이그런트에서 생성된 가상 머신에 ssh로 접속한다.
- vagrant provision
- 베이그런트에서 관리하는 가상 머신의 설정을 변경하고 적용한다.
Vagrant 실행하기
Vagrant를 통해 가상머신을 실행하기 위해 다음과 같이 설정을 진행한다.
$ mkdir vagrant_ubuntu && cd vagrant_ubuntu$ vagrant init
A `Vagrantfile` has been placed in this directory. You are now
ready to `vagrant up` your first virtual environment! Please read
the comments in the Vagrantfile as well as documentation on
`vagrantup.com` for more information on using Vagrant.Vagrant을 실행하기 위한 디렉터리를 생성하고 init 명령을 통해 Vagrantfile을 생성한다. 별다른 명령 없이 실행하면 기본 값으로 파일이 만들어진다. Vagrantfile의 내용은 다음과 같다.
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
# All Vagrant configuration is done below. The "2" in Vagrant.configure
# configures the configuration version (we support older styles for
# backwards compatibility). Please don't change it unless you know what
# you're doing.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
# The most common configuration options are documented and commented below.
# For a complete reference, please see the online documentation at
# https://docs.vagrantup.com.
# Every Vagrant development environment requires a box. You can search for
# boxes at https://vagrantcloud.com/search.
config.vm.box = "base"
# Disable automatic box update checking. If you disable this, then
# boxes will only be checked for updates when the user runs
# `vagrant box outdated`. This is not recommended.
# config.vm.box_check_update = false
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
# within the machine from a port on the host machine. In the example below,
# accessing "localhost:8080" will access port 80 on the guest machine.
# NOTE: This will enable public access to the opened port
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
# within the machine from a port on the host machine and only allow access
# via 127.0.0.1 to disable public access
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080, host_ip: "127.0.0.1"
# Create a private network, which allows host-only access to the machine
# using a specific IP.
# config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.33.10"
# Create a public network, which generally matched to bridged network.
# Bridged networks make the machine appear as another physical device on
# your network.
# config.vm.network "public_network"
# Share an additional folder to the guest VM. The first argument is
# the path on the host to the actual folder. The second argument is
# the path on the guest to mount the folder. And the optional third
# argument is a set of non-required options.
# config.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant_data"
# Provider-specific configuration so you can fine-tune various
# backing providers for Vagrant. These expose provider-specific options.
# Example for VirtualBox:
#
# config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
# # Display the VirtualBox GUI when booting the machine
# vb.gui = true
#
# # Customize the amount of memory on the VM:
# vb.memory = "1024"
# end
#
# View the documentation for the provider you are using for more
# information on available options.
# Enable provisioning with a shell script. Additional provisioners such as
# Ansible, Chef, Docker, Puppet and Salt are also available. Please see the
# documentation for more information about their specific syntax and use.
# config.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
# apt-get update
# apt-get install -y apache2
# SHELL
end
Vagrant는 루비로 만들어졌기 때문에 설정파일도 루비 문법으로 작성되어 있다. 길게 작성되어 있지만 주석이 대부분을 차지하기 때문에 줄이면 다음과 같다.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "base"
endconfig.vm.box = "base" 설정이 어떠한 이미지를 선택할지 정하는 것으로 이부분을 수정하면 Vagrant Cloud에서 만들어진 이미지를 다운로드 해서 실행한다. Vagrant는 이러한 이미지를 box라고 표현하며, 다음 링크를 통해 확인할 수 있다.
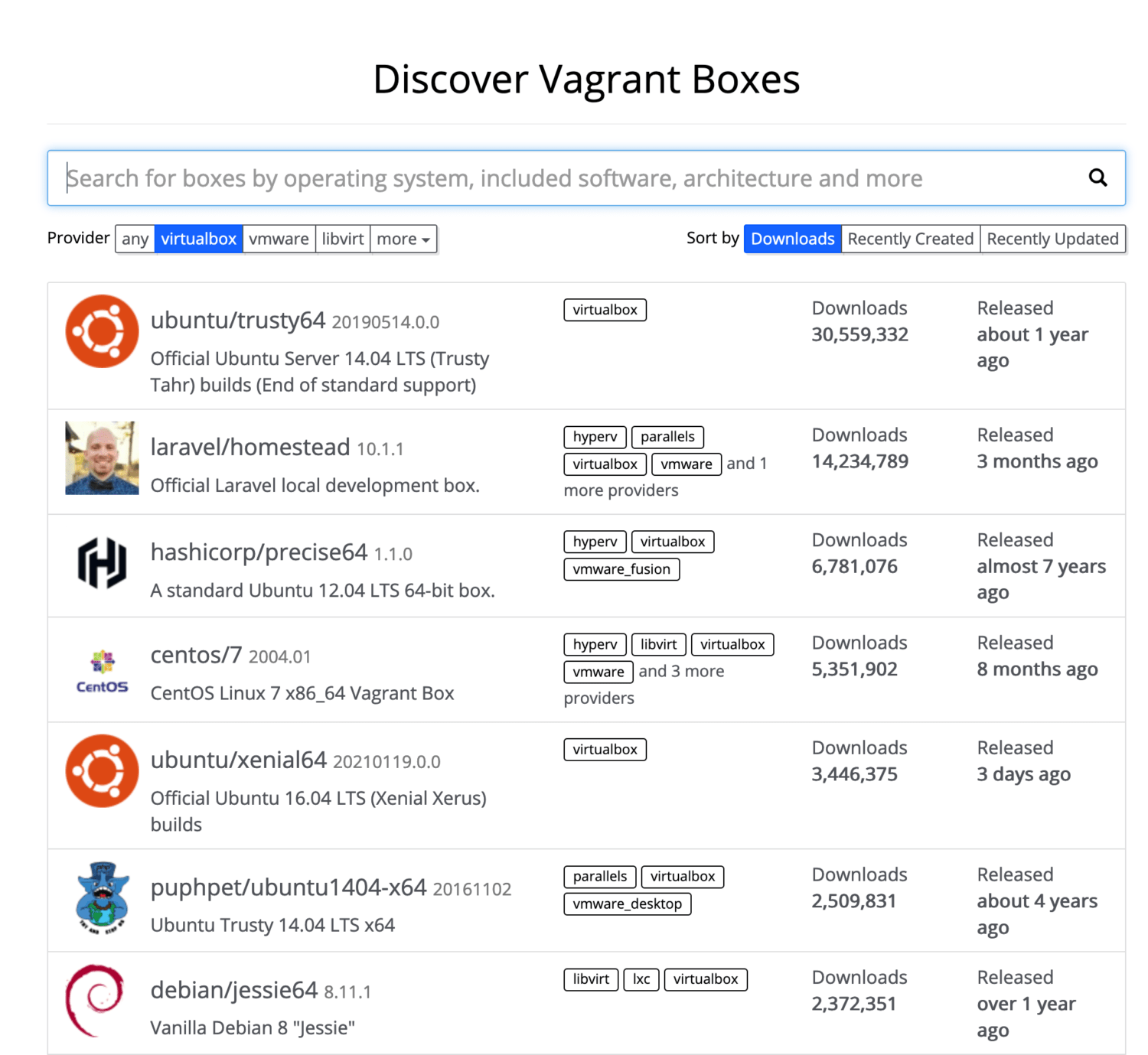
본 실습에서는 우분투 20.04 버전을 다운받아서 실행하도록 한다. 설정 파일에서 config.vm.box = "base" 부분을 config.vm.box = "ubuntu/focal64"으로 변경해준다. 이를 Vagrantfile로 표현하면 다음과 같다.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "ubuntu/focal64"
end위와 같은 방법과 다르게 초기화와 동시에 지정할 수 있는 방법은 다음과 같다.
$ vagrant init ubuntu/focal64준비과정은 끝났다. 최종적으로 Vagrant를 통해 VM을 실행하기 위해서 다음을 확인한다.
$ vagrant up
Bringing machine 'default' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
==> default: Importing base box 'ubuntu/focal64'...
==> default: Matching MAC address for NAT networking...
==> default: Checking if box 'ubuntu/focal64' version '20210125.0.1' is up to date...
==> default: Setting the name of the VM: vagrant_ubuntu_default_1612104035779_48475
==> default: Clearing any previously set network interfaces...
==> default: Preparing network interfaces based on configuration...
default: Adapter 1: nat
==> default: Forwarding ports...
default: 22 (guest) => 2222 (host) (adapter 1)
==> default: Running 'pre-boot' VM customizations...
==> default: Booting VM...
==> default: Waiting for machine to boot. This may take a few minutes...
default: SSH address: 127.0.0.1:2222
default: SSH username: vagrant
default: SSH auth method: private key
default:
default: Vagrant insecure key detected. Vagrant will automatically replace
default: this with a newly generated keypair for better security.
default:
default: Inserting generated public key within guest...
default: Removing insecure key from the guest if it's present...
default: Key inserted! Disconnecting and reconnecting using new SSH key...
==> default: Machine booted and ready!
==> default: Checking for guest additions in VM...
==> default: Mounting shared folders...
default: /vagrant => /Users/seongwon/Developments/vms/vagrant_ubuntu만약 실행과정에서 다음과 같은 에러가 발생하면 VirtualBox 재설치를 진행한다.
There was an error while executing `VBoxManage`, a CLI used by Vagrant
for controlling VirtualBox. The command and stderr is shown below.정상적으로 실행이 되었다면 다음 명령을 통해서 가상 머신에 접근할 수 있다.
$ vagrant ssh
Welcome to Ubuntu 20.04.1 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.4.0-64-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
System information as of Mon Feb 1 04:53:56 UTC 2021
System load: 0.18 Processes: 118
Usage of /: 3.2% of 38.71GB Users logged in: 0
Memory usage: 18% IPv4 address for enp0s3: 10.0.2.15
Swap usage: 0%
1 update can be installed immediately.
0 of these updates are security updates.
To see these additional updates run: apt list --upgradable
Last login: Sun Jan 31 14:41:37 2021 from 10.0.2.2
vagrant@ubuntu-focal:~$ lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 20.04.1 LTS
Release: 20.04
Codename: focal위와 같이 별다른 설정없이 간단한 코드 작성으로 VM이 생성되었고 이를 사용할 수 있는 환경이 갖추어졌다. 생성된 VM의 상태를 확인하고 종료 및 삭제하는 방법은 다음과 같다.
$ vagrant status
Current machine states:
default running (virtualbox)
The VM is running. To stop this VM, you can run `vagrant halt` to
shut it down forcefully, or you can run `vagrant suspend` to simply
suspend the virtual machine. In either case, to restart it again,
simply run `vagrant up`.
$ vagrant halt
==> default: Attempting graceful shutdown of VM...
$ vagrant status
Current machine states:
default poweroff (virtualbox)
The VM is powered off. To restart the VM, simply run `vagrant up`Vagrant는 Vagrantfile가 존재하는 디렉터리에 의존적이다. 또한 vagrant up 명령을 수행한 이후에는 가상 머신과 관련된 정보를 vagrant 디렉터리에 저장한다. SSH 접속에 관한 인증 정보도 같이 포함되어 있기 때문에 이를 삭제하게 되면 Vagrant가 정상적으로 동작하지 않는다.
이제 만들어진 VM을 삭제하는 명령은 다음과 같다.
$ vagrant destroy
default: Are you sure you want to destroy the 'default' VM? [y/N] y
==> default: Destroying VM and associated drives...Vagrant를 통해 만들어진 VM이 삭제되고, VirtualBox를 확인하면 삭제되어 있는 모습을 확인할 수 있다.
Vagrantfile 기초와 box
Vagrant가 동작하기 위해서는 이미지 형태인 box를 다운로드하여 실행하고, Vagrantfile이 이에 맞게 작성되어 있어야 한다. Vagrantfile은 루비로 작성되어 있으나 간단한 코드로 쉽게 수정할 수 있기 때문에 어렵지 않다. 먼저 자신의 머신에서 다운로드한 box 명령을 살펴본다.
$ vagrant box
Usage: vagrant box <subcommand> [<args>]
Available subcommands:
add
list
outdated
prune
remove
repackage
update
For help on any individual subcommand run `vagrant box <subcommand> -h`
--[no-]color Enable or disable color output
--machine-readable Enable machine readable output
-v, --version Display Vagrant version
--debug Enable debug output
--timestamp Enable timestamps on log output
--debug-timestamp Enable debug output with timestamps
--no-tty Enable non-interactive output명령어 자체가 간단하기 때문에 이해하는 게 크게 문제가 없을 것이다. 간단한 실습을 위해 현재 다운로드된 box를 확인하고 삭제해보도록 한다.
$ vagrant box list
ubuntu/focal64 (virtualbox, 20210125.0.1)
$ vagrant box remove ubuntu/focal64
Removing box 'ubuntu/focal64' (v20210125.0.1) with provider 'virtualbox'...
$ vagrant box list
There are no installed boxes! Use `vagrant box add` to add some.이제 Vagrantfile에 대해 조금 더 자세히 살펴본다.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "ubuntu/focal64"
end우리가 이전에 Vagrant를 실행하기 위해 만들어진 Vagrantfile를 살펴보면 Vagrant.configure("2")의 경우 Vagrant 설정 형식 버전 2를 사용한다는 의미 한다. 하위 버전과 호환을 위해 사용하지만 메이저 버전은 버전 2를 사용하는 것이 일반적이다. 이후 do...end 안에 Vagrant를 통해 설정할 정보를 입력한다. 즉 모든 설정 정보는 do...end 블록 안에 작성하면 된다.
최신 버전의 박스를 사용할 경우에는 버전을 기입하지 않아도 되지만 특별한 사유로 인해서 특정 버전을 사용하기 위해서는 다음과 같이 버전을 지정한다. 버전 정보는 Vagrant Cloud에서 자세히 확인할 수 있다.

위와 같이 버전을 확인하고 다음과 같이 파일을 작성한다.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "ubuntu/bionic64"
config.vm.box_version = "20210119.1.0"
end$ vagrant up
Bringing machine 'default' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
==> default: Box 'ubuntu/bionic64' could not be found. Attempting to find and install...
default: Box Provider: virtualbox
default: Box Version: 20210119.1.0
==> default: Loading metadata for box 'ubuntu/bionic64'
default: URL: https://vagrantcloud.com/ubuntu/bionic64
==> default: Adding box 'ubuntu/bionic64' (v20210119.1.0) for provider: virtualbox
default: Downloading: https://vagrantcloud.com/ubuntu/boxes/bionic64/versions/20210119.1.0/providers/virtualbox.box
Download redirected to host: cloud-images.ubuntu.com
==> default: Successfully added box 'ubuntu/bionic64' (v20210119.1.0) for 'virtualbox'!
==> default: Importing base box 'ubuntu/bionic64'...
==> default: Matching MAC address for NAT networking...
==> default: Checking if box 'ubuntu/bionic64' version '20210119.1.0' is up to date...
==> default: Setting the name of the VM: vagrant_ubuntu_default_1612157695873_6142
==> default: Clearing any previously set network interfaces...
==> default: Preparing network interfaces based on configuration...
default: Adapter 1: nat
==> default: Forwarding ports...
default: 22 (guest) => 2222 (host) (adapter 1)
==> default: Running 'pre-boot' VM customizations...
==> default: Booting VM...
==> default: Waiting for machine to boot. This may take a few minutes...
default: SSH address: 127.0.0.1:2222
default: SSH username: vagrant
default: SSH auth method: private key
default: Warning: Connection reset. Retrying...
default: Warning: Remote connection disconnect. Retrying...
default:
default: Vagrant insecure key detected. Vagrant will automatically replace
default: this with a newly generated keypair for better security.
default:
default: Inserting generated public key within guest...
default: Removing insecure key from the guest if it's present...
default: Key inserted! Disconnecting and reconnecting using new SSH key...
==> default: Machine booted and ready!
==> default: Checking for guest additions in VM...
default: The guest additions on this VM do not match the installed version of
default: VirtualBox! In most cases this is fine, but in rare cases it can
default: prevent things such as shared folders from working properly. If you see
default: shared folder errors, please make sure the guest additions within the
default: virtual machine match the version of VirtualBox you have installed on
default: your host and reload your VM.
default:
default: Guest Additions Version: 5.2.42
default: VirtualBox Version: 6.1
==> default: Mounting shared folders...
default: /vagrant => /Users/seongwon/Developments/vms/vagrant_ubuntu지정한 버전에 맞는 박스가 새롭게 다운로드하는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 이제 VM 성능에 관련된 설정을 변경하도록 한다. 다음과 같이 작성한다.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "ubuntu/bionic64"
config.vm.box_version = "20210119.1.0"
config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |machine|
machine.memory = 4096
machine.cpus = 4
end
end새로운 설정을 적용하기 위해서는 vagrant destroy을 통해 VM을 삭제하고 vagrant up 명령을 통해 다시 실행할 수 있지만 이 보다 간단하게 vagrant reload를 사용해도 된다.
$ vagrant reload
==> default: Attempting graceful shutdown of VM...
==> default: Checking if box 'ubuntu/bionic64' version '20210119.1.0' is up to date...
==> default: Clearing any previously set forwarded ports...
==> default: Clearing any previously set network interfaces...
==> default: Preparing network interfaces based on configuration...
default: Adapter 1: nat
==> default: Forwarding ports...
default: 22 (guest) => 2222 (host) (adapter 1)
==> default: Running 'pre-boot' VM customizations...
==> default: Booting VM...
==> default: Waiting for machine to boot. This may take a few minutes...
default: SSH address: 127.0.0.1:2222
default: SSH username: vagrant
default: SSH auth method: private key
default: Warning: Connection reset. Retrying...
default: Warning: Remote connection disconnect. Retrying...
==> default: Machine booted and ready!
==> default: Checking for guest additions in VM...
default: The guest additions on this VM do not match the installed version of
default: VirtualBox! In most cases this is fine, but in rare cases it can
default: prevent things such as shared folders from working properly. If you see
default: shared folder errors, please make sure the guest additions within the
default: virtual machine match the version of VirtualBox you have installed on
default: your host and reload your VM.
default:
default: Guest Additions Version: 5.2.42
default: VirtualBox Version: 6.1
==> default: Mounting shared folders...
default: /vagrant => /Users/seongwon/Developments/vms/vagrant_ubuntu
==> default: Machine already provisioned. Run `vagrant provision` or use the `--provision`
==> default: flag to force provisioning. Provisioners marked to run always will still run.
VirtualBox를 통해 생성된 VM을 확인하면 CPU와 메모리가 증가된 것을 확인할 수 있다. 이러한 설정 외에도 네트워크 설정, 디렉터리 지정, 개발 환경을 구축하기 위한 provision 설정을 진행할 수 있지만 이에 대한 설명은 다음에 자세히 진행하도록 한다.
Vagrant로 멀티 VM 생성하기
마지막으로 하나의 VM 생성이 아닌 여러 VM을 생성하여 개발환경을 간단하게 구축하는 방법을 살펴본다. 이해를 돕기 위해 프런트엔드 - 벡엔드 - 데이터베이스 - 파일서버 4개의 VM을 동시에 올리는 예제를 살펴보도록 하겠다.
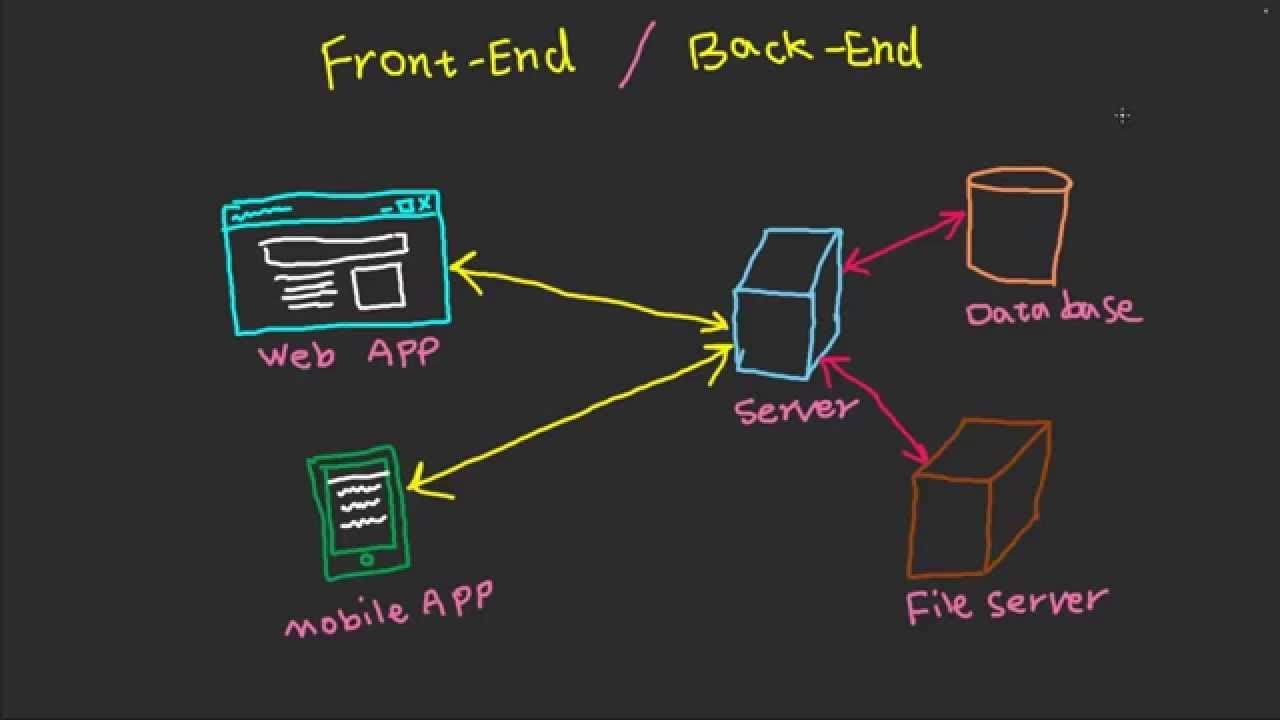
위에서 잠시 언급했듯이 Vagrantfile 정의를 통해 실행하고자 하는 개발환경을 한 번에 지정하고 연동할 수 있지만 간단한 실습을 목적으로 하기에 다른 연동 작업 없이 실행만 진행하도록 하겠다.
Vagrant를 통해 실행할 VM의 성능은 다음과 같이 지정한다고 가정한다. 만약 이를 다 수용하지 못하는 상황이라면 VM 성능을 수정한다.
- 프런트엔드 : Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
- CPU : v1 Core
- RAM : 1GB
- 벡엔드 : Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
- CPU : v2 Core
- RAM: 2GB
- 데이터베이스 : Fedora 33
- CPU: v4 Core
- RAM : 4GB
- 파일서버 : Centos 8
- CPU: v2 Core
- RAM : 2GB
위와 같은 설정으로 진행한다고 가정하면 Vagrantfile은 다음과 같이 작성할 수 있다.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.define "frontend" do |frontend|
frontend.vm.box = "ubuntu/bionic64"
frontend.vm.host_name = "front"
frontend.vm.provider :virtualbox do |spec|
spec.cpus = 1
spec.memory = 1024
end
end
config.vm.define "backend" do |backend|
backend.vm.box = "ubuntu/focal64"
backend.vm.host_name = "api"
backend.vm.provider :virtualbox do |spec|
spec.cpus = 2
spec.memory = 2048
end
end
config.vm.define "db" do |db|
db.vm.box = "generic/fedora33"
db.vm.host_name = "db"
db.vm.provider :virtualbox do |spec|
spec.cpus = 4
spec.memory = 4096
end
end
config.vm.define "file" do |file|
file.vm.box = "generic/centos8"
file.vm.host_name = "file"
file.vm.provider :virtualbox do |spec|
spec.cpus = 2
spec.memory = 2048
end
end
endfile.vm.host_name 부분은 VM 호스트 이름을 정하는 부분이며, 정상적으로 Vagrantfile 작성이 완료되었다면 4개의 VM이 성능에 맞춰서 실행된다.
$ vagrant up
.....
# 아래와 같이 각각의 VM에 접속할 수 있다.
$ vagrant ssh frontend
$ vagrant ssh backend
$ vagrant ssh db
$ vagrant ssh file 
Vagrant를 실행하면 VirtualBox에 4개의 VM이 우리가 설정한 성능으로 올라간 것을 최종 확인할 수 있다. 별도로 특정 VM에 사양을 조정하고 전체 VM에는 일괄적으로 성능을 정해야 한다면 다음과 같이 작성할 수 있다.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.define "master_server" do |master|
master.vm.box = "ubuntu/focal64"
master.vm.host_name = "master"
master.vm.provider :virtualbox do |spec|
spec.cpus = 4
spec.memory = 4096
end
end
config.vm.define "slave_server" do |slave|
slave.vm.box = "ubuntu/focal64"
slave.vm.host_name = "slave"
end
# 따로 cpu 갯수와 memory를 적지 않았다면, 기본으로 설정될 값
config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |spec|
spec.cpus = 2
spec.memory = 1024
end
end